Understanding Web Application Firewall (WAF)
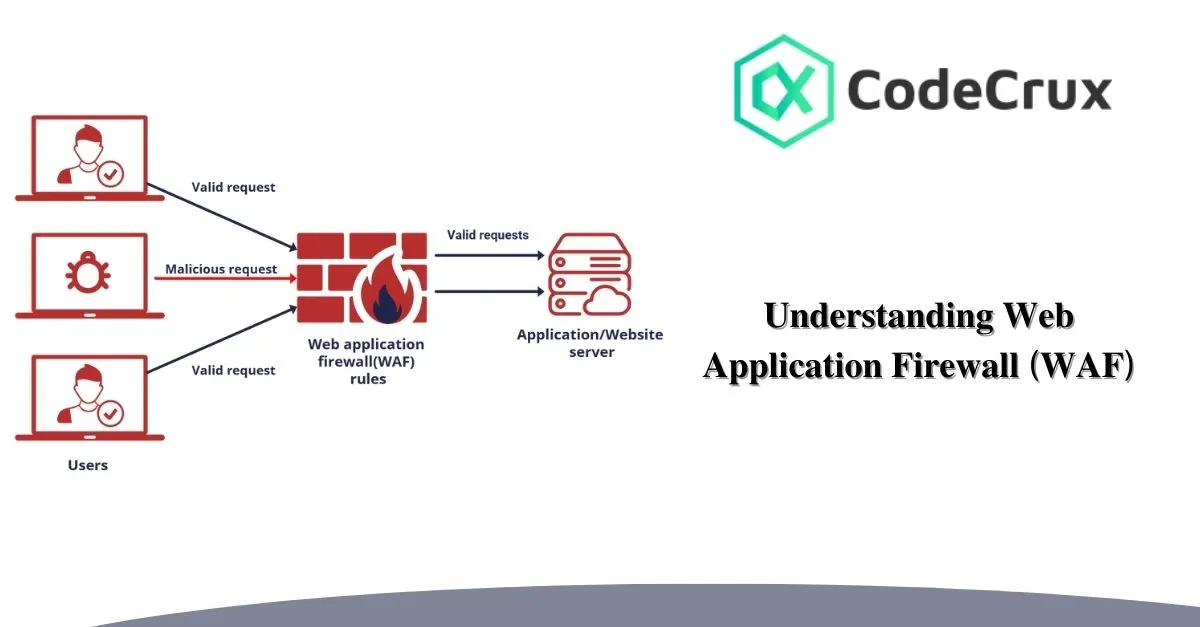
web applications are prime targets for cyber threats. From SQL injection to cross-site scripting (XSS), attackers are constantly evolving their methods to exploit vulnerabilities. To safeguard web applications against these threats, organizations rely on Web Application Firewalls (WAFs). A WAF acts as a shield between a web application and potential cyber threats, filtering, monitoring, and blocking malicious traffic before it reaches the application.
What is a Web Application Firewall (WAF)?
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security solution designed to protect web applications by analyzing HTTP traffic and blocking harmful requests. Unlike traditional firewalls that guard against network-level threats, a WAF operates at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model, ensuring web-specific security.
WAFs are essential in defending against attacks such as:
-
SQL Injection (SQLi) – Malicious SQL queries aimed at database exploitation.
-
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Injection of malicious scripts into web pages.
-
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) – Unauthorized commands executed on behalf of authenticated users.
-
Remote Code Execution (RCE) – Attackers injecting and executing malicious code on a server.
-
DDoS Attacks – Overwhelming web servers with excessive traffic.
How Does a WAF Work?
A WAF analyzes HTTP/S requests and applies predefined rulesets to identify and mitigate threats. It functions in three primary modes:
-
Blacklist-based (Negative Security Model) – Blocks traffic matching known attack signatures.
-
Whitelist-based (Positive Security Model) – Allows only predefined, trusted traffic.
-
Hybrid Approach – Combines both models for enhanced security and flexibility.
Deployment Modes
A WAF can be deployed in various ways, depending on an organization’s infrastructure:
-
Network-based WAF – Installed on-premises, requiring dedicated hardware.
-
Host-based WAF – Integrated into an application’s software stack, offering deep customization.
-
Cloud-based WAF – Managed by third-party security providers, offering scalability and ease of maintenance.
Key Features of an Effective WAF
A robust WAF provides multiple security layers to counter evolving cyber threats. Some key features include:
-
Real-time Threat Intelligence – Continuous updates to mitigate zero-day attacks.
-
Behavioral Analysis & Machine Learning – Detects anomalies and unknown attack patterns.
-
Rate Limiting & Bot Mitigation – Prevents automated attacks and brute-force attempts.
-
SSL/TLS Inspection – Decrypts and inspects encrypted traffic for threats.
-
Custom Rule Implementation – Allows organizations to define security policies based on specific needs.
-
Logging & Reporting – Provides visibility into traffic patterns and attack attempts.
Benefits of Implementing a WAF
1. Enhanced Security
A WAF protects against a wide range of OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities and other web-based threats, securing applications and sensitive data.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Many industries require WAFs for compliance with PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 to protect customer data and maintain trust.
3. Improved Application Performance
Cloud-based WAFs with caching and content optimization improve application speed while filtering out malicious requests.
4. Cost Savings
Preventing cyber threats reduces the risk of financial losses due to data breaches, downtime, and compliance violations.
Choosing the Right WAF
Selecting a WAF depends on factors like business size, web traffic volume, and security needs. When evaluating a WAF solution, consider:
-
Deployment Flexibility – On-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid options.
-
Scalability – Ability to handle increasing traffic loads.
-
Integration – Compatibility with existing security infrastructure (SIEM, IAM, etc.).
-
Ease of Management – Intuitive dashboard and automated updates.
Conclusion
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a crucial component of modern cybersecurity strategies, offering protection against sophisticated web attacks. By implementing a WAF, organizations can safeguard their applications, ensure regulatory compliance, and enhance overall security posture.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must adopt proactive security measures like WAFs to stay ahead of attackers and maintain robust protection for their web applications.